Blog
Behavioral Segmentation: Everything You Need to Know
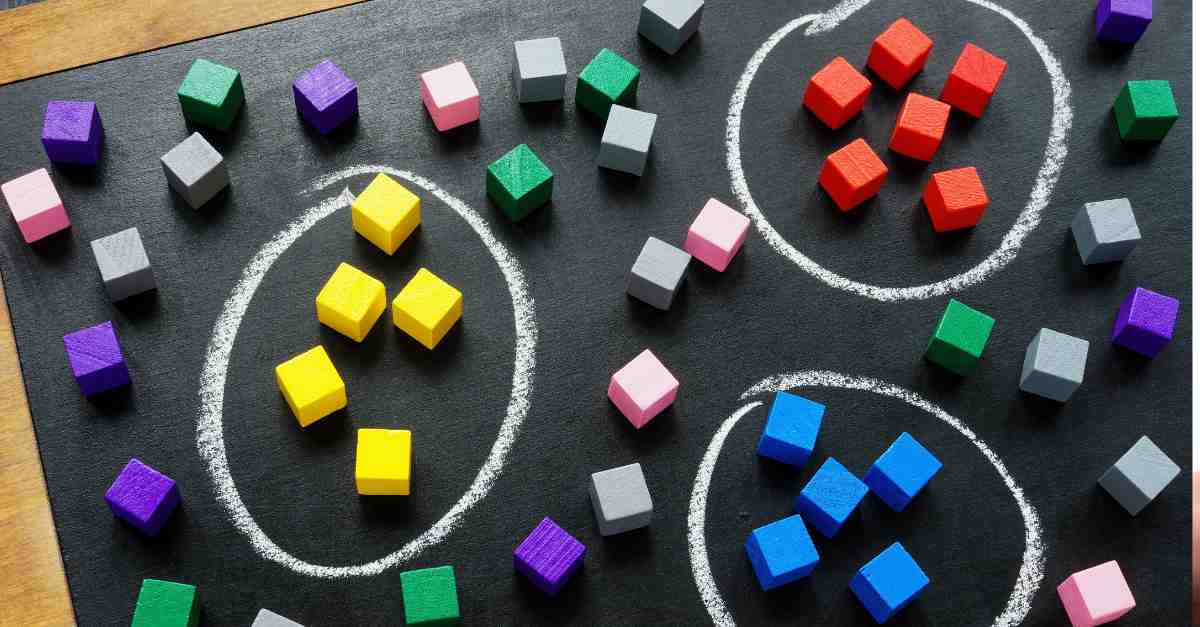


Data Collection Methods
To gather behavioral data, companies can employ various methods:
- Website and app analytics: Track user interactions, page views, and click-through rates.
- Purchase history: Analyze transaction data, including frequency, recency, and monetary value.
- Customer feedback: Collect insights through surveys, reviews, and customer support interactions.
- Social media monitoring: Observe brand mentions, engagement, and sentiment across platforms.
- Email engagement: Monitor open rates, click-throughs, and response rates to campaigns.
Tools and Technologies
Several tools can facilitate behavioral segmentation:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems: These serve as vital tools for tracking and analyzing customer actions across various touchpoints.
- Analytics platforms: Tools like Google Analytics or Amplitude provide detailed insights into user behavior on websites and apps.
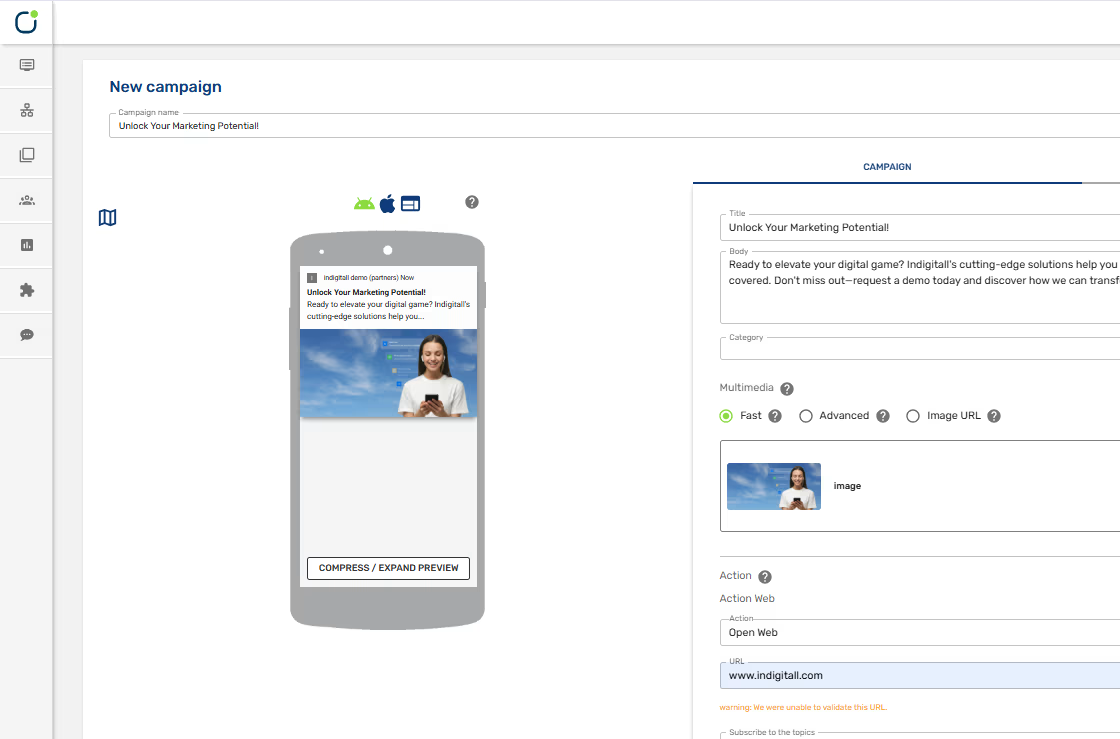
- Customer Engagement Platforms: Using tools like indigitall to communicate with your customers across all channels can help .
- Machine learning algorithms: Tools like indigitall include machine learning and ai which can help boost the efficiency of the segmentation process and optimize sales and marketing endeavors.
Key Metrics to Track
When implementing behavioral segmentation, focus on these essential metrics:
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- Purchase frequency and recency
- Average order value
- Churn rate
- Engagement rate (e.g., app usage, email opens)
- Conversion rate
- Time spent on site/app
- Feature adoption rate
Creating Customer Personas
Developing customer personas based on behavioral data involves:
- Identifying common behavioral patterns among user groups
- Combining behavioral data with demographic and psychographic information
- Creating detailed profiles that include:
- Typical behaviors and actions
- Preferences and pain points
- Goals and motivations
- Preferred communication channels
- Validating personas through customer interviews or surveys
- Regularly updating personas based on new behavioral data
By following these steps and utilizing the right tools, businesses can effectively implement behavioral segmentation to create more targeted, personalized marketing strategies that resonate with their audience and drive better results.
Strategies for Effective Behavioral Segmentation
To maximize the impact of behavioral segmentation, marketers should employ a range of strategies that focus on identifying valuable segments, tailoring messages, personalizing experiences, and continuously optimizing efforts.
Identifying Valuable Segments
- Analyze customer lifetime value (CLV): Focus on segments with the highest potential for long-term profitability.
- Utilize RFM analysis: Segment customers based on Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value of their purchases.
- Conduct cohort analysis: Group customers based on shared characteristics or experiences over time.
- Implement predictive modeling: Use machine learning algorithms to identify segments likely to respond positively to marketing efforts.
- Assess segment size and growth potential: Prioritize segments that offer scalable opportunities.
Tailoring Marketing Messages
- Develop segment-specific value propositions: Craft messaging that addresses the unique needs and preferences of each segment.
- Use appropriate tone and language: Adjust communication style to resonate with different behavioral segments.
- Highlight relevant features or benefits: Focus on aspects of your product or service that are most appealing to each segment.
- Create targeted content: Develop blog posts, videos, or infographics that address specific behavioral segment interests.
- Customize call-to-actions (CTAs): Design CTAs that align with the typical behavior and motivations of each segment.
Personalization Techniques
- Dynamic content: Implement website or email content that changes based on user behavior or preferences.
- Product recommendations: Use collaborative filtering or content-based filtering to suggest relevant products.
- Behavioral triggers: Set up automated messages or actions based on specific user behaviors.
- Personalized pricing: Offer dynamic pricing or promotions based on individual user behavior and purchase history.
- Custom user journeys: Create tailored onboarding experiences or app interfaces based on user behavior and preferences.
A/B Testing and Optimization
- Test omnichannel messaging variations: Compare different headlines, copy, or offers to see which resonates best with each segment.
- Experiment with design elements: Test various layouts, colors, or images to optimize visual appeal for different segments.
- Optimize timing and frequency: Test different send times for emails or frequency of retargeting ads for each segment.
- Compare channel effectiveness: Evaluate which marketing channels work best for different behavioral segments.
- Continuous iteration: Regularly analyze test results and implement improvements based on findings.
- Multi-variate testing: Test multiple variables simultaneously to identify optimal combinations for each segment.
By implementing these strategies, marketers can effectively leverage behavioral segmentation to create more targeted, personalized, and impactful marketing campaigns. Remember that behavioral segmentation is an ongoing process, requiring constant refinement and adaptation as customer behaviors evolve and new data becomes available.
Advanced Strategies for Behavioral Segmentation
As behavioral segmentation evolves, marketers are employing increasingly sophisticated techniques to gain deeper insights and create more personalized experiences. Here are some advanced strategies:
Predictive Behavioral Segmentation
Predictive behavioral segmentation uses machine learning algorithms to forecast future customer behaviors based on historical data. This approach allows marketers to anticipate customer needs and actions.
- Using machine learning to forecast future behaviors: Algorithms analyze past purchase patterns, browsing history, and engagement metrics to predict future actions.
- Implementing predictive models for customer lifetime value: These models estimate the total value a customer will bring to a business over their entire relationship.
Cross-Channel Behavioral Segmentation
This strategy involves tracking and analyzing customer behavior across multiple touchpoints to create a comprehensive view of the customer journey. indigitall’s omnichannel platform is ideal for this use case giving you a clear picture of your customer’s journey across all channels.
- Tracking customer behavior across multiple touchpoints: Includes website interactions, mobile app usage, in-store visits, and social media engagement.
- Integrating data from various sources: Combines data from CRM systems, web analytics, point-of-sale systems, and marketing automation platforms.
- Strategies for creating a unified customer view: Implementing customer data platforms (CDPs) to consolidate and harmonize data from different sources.
Real-Time Behavioral Segmentation
Real-time segmentation allows marketers to respond immediately to customer actions, creating highly relevant and timely interactions.
- Importance of immediate segmentation in digital marketing: Enables instant personalization and timely interventions based on current customer behavior.
- Technologies enabling real-time segmentation: Includes stream processing technologies, real-time analytics platforms, and AI-powered decision engines.
- Applications: Personalized content delivery on websites, dynamic pricing in e-commerce, and instant offer generation in mobile apps.
Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation involves breaking down broad customer segments into highly specific, granular groups based on detailed behavioral patterns.
- Breaking down broad segments into highly specific groups: Creates extremely targeted segments based on specific behaviors, preferences, and needs.
- Benefits and challenges: Enables hyper-personalization but can be complex to manage and implement at scale.
- Tools and techniques: Advanced analytics platforms, AI-driven segmentation tools, and customer data platforms with robust segmentation capabilities.
AI-Powered Behavioral Clustering
This approach uses unsupervised machine learning algorithms to discover hidden patterns in customer behavior data.
- Unsupervised learning for discovering hidden behavioral patterns: Algorithms identify natural groupings in data without predefined categories.
- Advantages over traditional rule-based segmentation: Can uncover unexpected insights and adapt to changing customer behaviors automatically.
- Implementing AI clustering algorithms: Utilizes techniques like k-means clustering, hierarchical clustering, and neural network-based clustering in marketing automation platforms.
Sequential Behavioral Segmentation
This strategy focuses on analyzing the sequence of actions customers take over time, providing insights into the customer journey.
- Analyzing customer journeys and behavior sequences: Maps out the typical paths customers take from awareness to purchase and beyond.
- Identifying critical touchpoints and decision moments: Pinpoints key interactions that influence customer decisions.
- Applying sequential segmentation in omnichannel marketing: Tailors marketing strategies based on the customer’s position in their journey across multiple channels.
By implementing these advanced strategies, marketers can create more nuanced, effective, and personalized marketing campaigns that resonate with their audience on a deeper level.
Real-World Applications of Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation has proven to be a powerful tool across various marketing disciplines. Here’s how it’s applied in different areas:
E-commerce
In the e-commerce sector, behavioral segmentation is crucial for personalizing the shopping experience and increasing conversions.
- Product recommendations: Analyze browsing and purchase history to suggest relevant products.
- Abandoned cart recovery: Target users who left items in their cart with personalized reminders and incentives.
- Dynamic pricing: Adjust prices based on user behavior, demand, and inventory levels.
- Personalized homepage: Customize the layout and featured products based on individual user preferences and past interactions.
Example: Amazon uses behavioral segmentation to power its “Customers who bought this item also bought” feature, which reportedly drives 35% of its sales.
Content Marketing
Behavioral segmentation helps content marketers deliver more relevant and engaging content to their audience.
- Content personalization: Tailor blog posts, videos, and infographics based on user interests and engagement patterns.
- Topic selection: Use behavioral data to identify popular topics and content formats among different segments.
- Content distribution: Choose the most effective channels and timing for content delivery based on user behavior.
- Lead nurturing: Create targeted content journeys based on a user’s interaction with previous content pieces.
Example: Netflix uses behavioral data to personalize not just content recommendations but also the artwork displayed for each show or movie.
Email Campaigns
Behavioral segmentation significantly improves the effectiveness of email marketing efforts.
- Triggered emails: Send automated emails based on specific user actions or inactions.
- Personalized content: Customize email content based on past purchases, browsing history, and engagement levels.
- Frequency optimization: Adjust email frequency based on individual user engagement patterns.
- Re-engagement campaigns: Target inactive users with tailored content to bring them back.
Example: Spotify sends personalized “Discover Weekly” playlists via email, based on each user’s listening history and preferences.
Product Development
Behavioral data can inform product teams about user needs and preferences, guiding feature development and improvements.
- Feature prioritization: Focus on developing features that behavioral data shows are most used or requested.
- User experience optimization: Improve product interfaces based on observed user behavior and pain points.
- Beta testing: Select participants for beta programs based on their usage patterns and engagement levels.
- Product roadmap planning: Use behavioral insights to inform long-term product strategy and innovation.
Example: Fitness app Strava uses behavioral data to identify which features are most valued by different user segments, informing their product development priorities.
Customer Retention
Behavioral segmentation plays a crucial role in strategies aimed at reducing churn and increasing customer loyalty.
- Churn prediction: Identify at-risk customers based on changes in their behavior patterns.
- Loyalty programs: Design and tailor rewards based on individual customer behaviors and preferences.
- Proactive support: Reach out to users who exhibit behaviors indicating they might need assistance.
- Upselling and cross-selling: Offer relevant upgrades or complementary products based on usage behavior.
Example: Telecom companies use behavioral data to predict which customers are likely to switch providers and target them with retention offers.
By applying behavioral segmentation across these areas, businesses can create more targeted, relevant, and effective marketing strategies. This approach not only improves customer experience but also drives better business outcomes, from increased sales and customer loyalty to more efficient resource allocation and product development.
Challenges and Limitations of Behavioral Segmentation
While behavioral segmentation offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges and limitations. Understanding these is crucial for effective implementation and ethical use of this marketing strategy.
Data Privacy Concerns
As behavioral segmentation relies heavily on collecting and analyzing personal data, privacy concerns are at the forefront of challenges.
- Regulatory compliance: Adhering to data protection regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and others can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Consumer trust: Excessive data collection or perceived misuse can erode customer trust and damage brand reputation.
- Data security: Protecting large volumes of sensitive behavioral data from breaches and unauthorized access is an ongoing challenge.
Mitigation strategies:
- Implement robust data protection measures
- Be transparent about data collection and usage policies
- Offer customers control over their data, including opt-out options
Overcoming Data Silos
Many organizations struggle with fragmented data across different departments and systems, hindering effective behavioral segmentation.
- Inconsistent data: Different systems may have conflicting or outdated information about the same customer.
- Incomplete view: Siloed data prevents a holistic understanding of customer behavior across all touchpoints.
- Integration challenges: Technical difficulties in merging data from various sources can impede segmentation efforts.
Mitigation strategies:
- Implement a centralized customer data platform (CDP)
- Foster cross-departmental collaboration and data sharing
- Invest in data integration and cleansing technologies
Balancing Personalization and Privacy
Finding the right balance between delivering personalized experiences and respecting customer privacy is a delicate task.
- Creep factor: Overly personalized messaging can feel intrusive and alienate customers.
- Consent management: Ensuring proper consent for data usage while maintaining effective personalization can be challenging.
- Ethical considerations: Determining the appropriate level of influence based on behavioral data raises ethical questions.
Mitigation strategies:
- Adopt a “privacy by design” approach in marketing strategies
- Be transparent about how personalization works and its benefits to customers
- Provide easy-to-use privacy controls for customers
Keeping Segmentation Models Up-to-Date
Customer behaviors and preferences change over time, requiring constant updates to segmentation models.
- Data decay: Behavioral data can quickly become outdated, leading to inaccurate segmentation.
- Changing market conditions: External factors like economic changes or new competitors can alter customer behaviors rapidly.
- Resource intensity: Continuously updating and validating segmentation models requires significant time and expertise.
Mitigation strategies:
- Implement machine learning models that can adapt to changing behaviors
- Regularly review and refresh segmentation criteria
- Conduct periodic customer research to validate and update behavioral insights
Additional Considerations
- Over-reliance on historical data: Past behavior doesn’t always predict future actions, especially in rapidly changing markets.
- Complexity of implementation: Sophisticated behavioral segmentation can be technically challenging and resource-intensive to implement.
- Interpretation challenges: Correctly interpreting behavioral data and translating it into actionable insights requires specialized skills.
By acknowledging these challenges and limitations, marketers can approach behavioral segmentation more realistically and ethically. Implementing robust strategies to address these issues will lead to more effective and responsible use of behavioral segmentation in marketing efforts.
Future Trends in Behavioral Segmentation
As technology continues to evolve, behavioral segmentation is poised for significant advancements. These emerging trends are set to revolutionize how businesses understand and interact with their customers.
AI and Machine Learning Applications
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are at the forefront of behavioral segmentation innovations, this trend will continue to grow as the technology advances and adapts. Here are are some examples of future trends:
- Advanced pattern recognition: AI algorithms can identify complex behavioral patterns that humans might miss, leading to more nuanced segmentation.
- Automated segmentation: Machine learning models can continuously update and refine segments without human intervention, ensuring they remain relevant.
- Predictive behavior modeling: AI can forecast future customer behaviors based on historical data and current trends.
Example: Netflix uses AI to analyze viewing habits and create micro-segments, allowing for hyper-personalized content recommendations.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics takes behavioral segmentation from descriptive to prescriptive, enabling businesses to anticipate customer needs and actions.
- Churn prediction: Identify customers at risk of leaving before they actually do.
- Lifetime value forecasting: Predict the long-term value of customers based on their behavioral patterns.
- Next best action: Determine the most effective next step in customer engagement for each segment.

Omnichannel Behavioral Analysis
Tools like indigitall are continuing to revolutionize how brands are interacting with their customers enabling them to do more and more advanced content delivery.
- Unified customer profiles: Integrate data from various channels (web, mobile, in-store, social media) to create comprehensive customer profiles.
- Journey mapping: Analyze customer behavior across different channels to understand the full customer journey.
- Omnichannel personalization: Deliver consistent, personalized experiences across all channels based on behavioral insights.
Real-Time Segmentation
The ability to segment customers in real-time allows for immediate, contextually relevant interactions.
- Dynamic segmentation: Instantly update customer segments based on their current behavior.
- Contextual marketing: Deliver personalized messages or offers based on the customer’s immediate context (location, time, current activity).
- Adaptive user experiences: Modify website or app interfaces in real-time based on user behavior.
Example: Sephora’s Virtual Artist tool uses real-time behavioral data to offer personalized makeup recommendations as customers interact with the app.
These trends highlight the move towards more sophisticated, dynamic, and personalized approaches to behavioral segmentation. As these technologies mature, businesses will be able to create increasingly targeted and effective marketing strategies, enhancing customer experiences and driving business growth.
How indigitall Can Enhance Your Behavioral Segmentation Efforts
Indigitall offers powerful tools and features to maximize the effectiveness of your behavioral segmentation strategies:
Advanced Data Collection and Analysis
Indigitall’s platform enables comprehensive data collection across multiple touchpoints, including web, mobile, and in-app interactions. This rich dataset forms the foundation for sophisticated behavioral analysis.
- Real-time tracking: Capture user behaviors as they happen, allowing for immediate segmentation and response.
- Cross-channel data integration: Combine data from various sources to create a unified view of customer behavior.
Dynamic Segmentation Capabilities
Leverage indigitall’s AI-powered segmentation engine to create highly specific and relevant customer segments.
- Automated segment creation: The system can automatically identify and create segments based on emerging behavioral patterns.
- Flexible segmentation criteria: Easily combine multiple behavioral factors to create nuanced segments.
Personalized Messaging and Campaigns
Indigitall’s messaging capabilities allow you to act on your behavioral insights effectively.
- Triggered messaging: Set up automated messages based on specific user behaviors or segment membership.
- Omni-channel delivery: Reach your segments through their preferred channels, whether it’s push notifications, in-app messages, or email.
Real-Time Optimization
Continuously improve your segmentation and marketing efforts with indigitall’s real-time analytics and A/B testing features.
- Performance tracking: Monitor the effectiveness of your behavioral segments and associated campaigns in real-time.
- A/B testing: Easily test different messaging approaches for each behavioral segment to optimize engagement.
By leveraging indigitall’s comprehensive suite of tools, marketers can take their behavioral segmentation to the next level, creating more targeted, effective, and personalized marketing campaigns that drive engagement and conversions.
Conclusion
Behavioral segmentation is a powerful strategy that enables marketers to understand their customers on a deeper level by analyzing their actions, preferences, and interactions. By leveraging behavioral insights, businesses can create highly targeted and personalized marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer segments, ultimately driving engagement, loyalty, and revenue.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding Behavioral Segmentation: It involves categorizing customers based on their behaviors rather than static characteristics, allowing for more dynamic and actionable insights.
- Types of Segmentation: Various types of behavioral segmentation—such as purchasing behavior, usage behavior, occasion-based segmentation, and customer journey stage—provide marketers with multiple lenses through which to analyze customer interactions.
- Implementation Strategies: Successful implementation requires effective data collection methods, the right tools and technologies, and the ability to create detailed customer personas based on behavioral data.
- Advanced Techniques: Emerging trends like predictive analytics, AI-powered clustering, and real-time segmentation are enhancing the sophistication of behavioral segmentation strategies.
- Real-World Applications: Behavioral segmentation can be applied across various marketing channels including e-commerce, content marketing, email campaigns, product development, and customer retention strategies.
- Challenges to Address: Marketers must navigate challenges such as data privacy concerns, data silos, balancing personalization with privacy, and keeping segmentation models up-to-date.
- Future Opportunities: As technology continues to evolve, the future of behavioral segmentation looks promising with advancements in AI, machine learning, and cross-channel analysis paving the way for even more personalized customer experiences.
By embracing behavioral segmentation and staying attuned to its evolving landscape, businesses can enhance their marketing effectiveness and foster stronger connections with their customers. As you move forward in your marketing efforts, consider how you can implement these insights to create more meaningful interactions that drive results.